[E-Health #2] All about tele-expertise



This week in “e-Health”, we discuss the subject of tele-expertise. Initially created for the follow-up of patients in institutions for the elderly, tele-expertise now concerns all patients. Tele-expertise is a real challenge for improving the healthcare system and access to care for all. Definition, functioning, fees, advantages and implementation… you will find in this article all you need to know about tele-expertise.
As defined in the French Public Health Code, the purpose of tele-expertise “is to enable a health professional to seek the opinion of one or more medical professionals at a distance because of their training or particular skills, on the basis of health information related to the management of a patient”.
In simple terms, a “requesting” physician wants a colleague’s opinion on a patient’s medical situation. Tele-expertise allows him to send all the patient’s data to the requested professional in a secure manner. The requested professional examines the information and provides his expertise to the requesting physician.
Unlike teleconsultation, exchanges are not necessarily made via videoconferencing and take place outside of any patient appointment. In concrete terms, tele-expertise is an exchange of opinions via a secure messaging system, at a distance, between healthcare professionals.
Any doctor can use tele-expertise, regardless of his sector, specialty or place of practice (city practice, EHPAD, hospital, clinic, health center, etc.). In addition, discussions are currently taking place on the possibility of extending the use of tele-expertise to other health professions such as nurses, for example.
Initially, this act was reserved for certain patients whose state of health or geographical situation justified easier access to care. This concerned patients with long-term illnesses, those suffering from rare diseases, those living in “under-dense” areas, those living in nursing homes and those in prison.
Since September 2021, the use of paid tele-expertise is possible for all patients.
Currently, there are two types of tele-expertise: level 1 and level 2. The level varies according to the complexity of the patient’s file and the frequency.
Level 1
A tele-expertise is considered level 1 when it is a “simple” question and the patient’s medical situation does not require an in-depth study. This may be, for example:
Level 2
A level 2 tele-expertise concerns a complex medical situation for which an in-depth study is required. This can be for example :
Rider No. 9 to the 2016 medical agreement calls for “simplifying and facilitating the use of tele-expertise and anchoring this type of practice among physicians” by changing the levels of tele-expertise. Starting in April 2022, there will be a single level of tele-expertise.
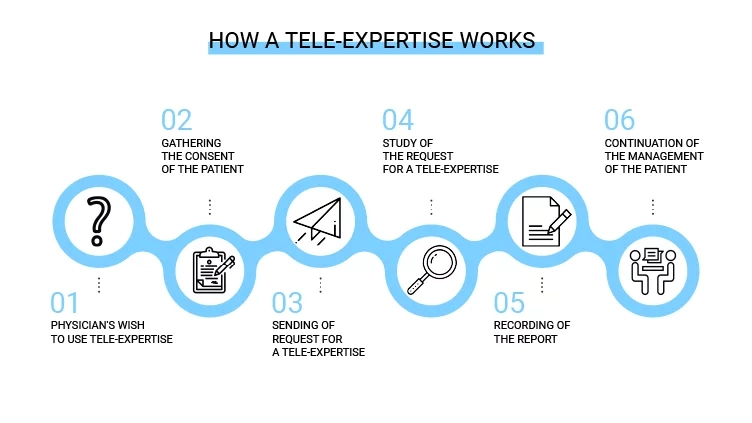
Step 1 – Physician’s desire to use tele-expertise
Following a medical appointment with a patient, the health professional may decide to call on a colleague to obtain his opinion on the situation. The use of remote expertise must be initiated by the requesting physician. However, the performance of the tele-expertise is the sole responsibility of the physician who is requested.
Step 2 – Gather patient consent
The requesting physician must first obtain the patient’s consent before referring the patient to another health care professional in any medical situation.
Step 3 – Transmission of the request
Once the patient’s consent has been obtained, the physician can then make a request for a tele-expertise to the requested professional. The request must be accompanied by all the information available to the physician that is necessary for the tele-expertise to be carried out (medical records, reports, images, test results, etc.).
Step 4 – The requested health professional reviews the request from the requesting physician
After analyzing the tele-expertise request, the requested professional decides if it is necessary or not.
→ If the tele-expertise is not feasible, the decision is notified in the patient’s file. The requesting physician will then offer the patient appropriate treatment.
→ If the tele-expertise is feasible, a response time is set and the patient is informed of the delay in obtaining the results.
Step 5 – Recording of the report
At the end of the tele-expertise, the health professional requested will draw up a report. This report will be recorded in the patient’s file as well as in the shared medical file if the patient has one. This report will also be transferred to the attending physician and to the requesting physician (if different from the attending physician) via a secure messaging system.
Step 6 – Continued management of the patient
The requesting physician contacts the patient in order to debrief him on the tele-expertise and guide him in the next steps of his care.
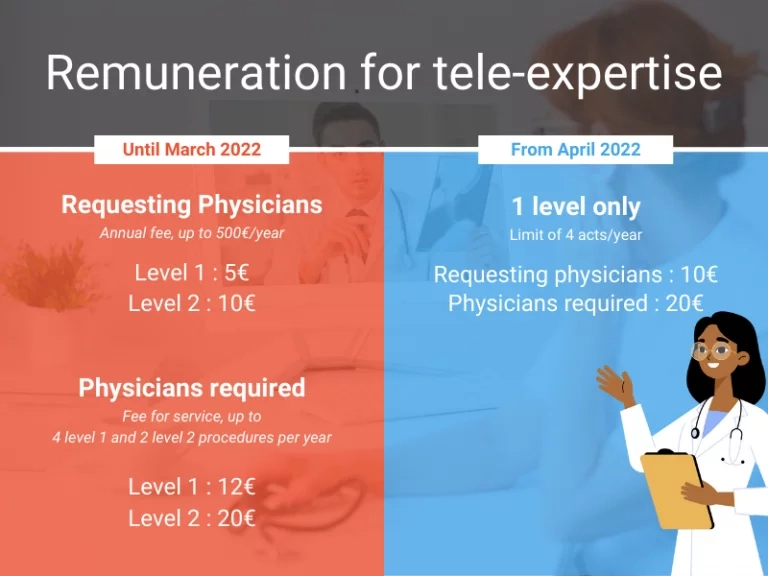
Healthcare professionals, whether they are requesting or requested, are remunerated during a remote expertise. Remuneration is calculated according to the complexity of the patient’s file (level 1 or level 2) and its frequency.
The requesting professional has an annual fee. He is paid 5€ per level 1 tele-expertise and 10€ per level 2 tele-expertise, up to a maximum of €500 per year.
For the required professional, on the other hand, it is a fee-for-service. The remuneration is 12€ per level 1 tele-expertise, within the limit of 4 acts per year, per doctor, for the same patient and 20€ per level 2 tele-expertise, within the limit of 2 acts per year, per doctor, for the same patient.
As previously mentioned, tele-expertise will only have one level from April 2022. This means that the remuneration will be modified in this sense. Only one level of remuneration will be applicable to all tele-expertise:
Tele-expertise performed is covered by French health insurance as of February 10, 2019.
Regarding billing, it is up to the professional who is requested to bill for the procedure, specifying the level of teleexpertise. French health insurance calculates the remuneration of the requesting professional based on his billing. The requested professional is paid within a few days, while the requesting professional is paid for all his or her requests at the beginning of the following year. For private physicians, tele-expertise is billed directly to French health insurance.
From April 2022, billing will also change as the requesting professional will also be able to bill for the procedure.
Tele-expertise meets the same requirements as a physical medical act (laws and regulations applicable to the conditions of practice, rules of ethics and standards of clinical practice). However, the regulations include additional requirements specific to telemedicine:
Free and informed consent of the patient
Gathering the patient’s consent before the procedure is performed is mandatory. Furthermore, the physician can also go further by explaining to the patient the principle, the procedure and the cost of a tele-expertise. He can also reassure the patient about the technologies used, the confidentiality of the exchanges and the security of the data.
Conditions for performing the procedures
A tele-expertise procedure must be performed under conditions that ensure:
Maintenance of patient records
Each healthcare professional involved in the act must record in the patient’s file:
Compliance with the terms of hosting personal health data
Healthcare professionals and organizations must ensure that the technology used complies with the provisions of the French Public Health Code regarding the security and hosting of healthcare data.
By putting different health professionals in contact with each other at a distance, teleexpertise helps to combat the lack of professionals in the country and considerably reduces waiting times for specialist advice. In addition, it promotes continuity of care by reducing the often long delays in obtaining an appointment with certain specialists.
Benefits for healthcare professionals

Tele-expertise offers several advantages to healthcare professionals. First of all, it gives the requesting physician the opportunity to gather precise information and an expert opinion. This allows him to support his diagnosis, provide a better response to the patient’s problem, and thus provide better care for his patient. For the requesting physician, tele-expertise represents a less time-consuming solution that is easy to integrate into his activity. Indeed, when he receives one or more requests, he can prioritize them and integrate them into his agenda as he wishes. Finally, a common advantage for healthcare professionals, whether they are requesting or requested, is the sharing and transmission of knowledge. Indeed, remote expertise brings together healthcare professionals who do not share the same specialty. Thus, it encourages interaction between colleagues, the pooling of knowledge and, in the long run, improves the skills of each.
Benefits for patients

For patients, the benefits of tele-expertise are also numerous. To begin with, it provides better access to care for patients and facilitates continuity of care. Indeed, a patient can easily decide to renounce care if he lives in an under-densified area, if the delay in obtaining an appointment is too long, if the available physician is far from his home, etc. Tele-expertise can replace a specialized consultation, shorten the time it takes to obtain an answer and offer patients a qualified opinion.
As previously mentioned, tele-expertise does not necessarily require exchanges via videoconference. It can be carried out asynchronously via a simple secure messaging system or synchronously via a video solution. However, videoconferencing for tele-expertise is relatively advantageous for medical professionals and patients. Asynchronous tele-expertise requires physicians to make several round trips in certain complex cases. However, using a videoconference allows the patient’s case to be treated in a single exchange. In addition, real-time video allows for more interaction and knowledge sharing between colleagues, which is a real advantage. In addition, when people speak orally, the information exchanged is much more complete and accurate. This can lead to a more accurate diagnosis and therefore, to a better treatment and follow-up of the patient.

There are many video conferencing solutions on the market, but many are not adapted to tele-expertise. In order to choose the most appropriate videoconferencing solution, you must consider two essential elements: security and features.
The security
The chosen solution must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and host personal health data in a suitable storage environment.
The features
The solution must be adapted to the use of tele-expertise. For this, several features must be considered when choosing the solution.
Did you like this first article? We’ll see you next month for a new article on telecare. In the meantime, do not hesitate to discover the 1st article of the series on teleconsultation.
Are you looking for a tele-expertise solution? Discover Apizee Health, our French and secure turnkey solution or as an API to be integrated. Already used by the GCS e-Santé Bretagne, Innovation e-Santé Sud, the Service de Santé des Armées and the Brigade des sapeurs-pompiers de Paris, Apizee Health is a solution that requires no installation and is quick to deploy. Contact us for a demo of the solution.
Read also:
Explore key findings from the Genesys State of Customer Experience report. Learn how AI, omnichannel strategies, and video chat are transforming CX and enhancing customer satisf...
The State of Customer Experience report by Genesys : Key Insights and Trends
27 Mar 2025
Despite AI and automation, customers still prefer to speak to a human for support. Discover why human interaction remains essential for great customer service.
Why Customers Still Want to Speak to a Human in Customer Service
17 Mar 2025
Discover the top customer experience influencers in Europe, shaping the future of CX and customer service.
Top 100 Customer Experience Influencers to follow
10 Mar 2025
Interested in our solutions?