WebSocket vs WebRTC: A Comprehensive Comparison


In the ever-evolving landscape of digital communication, understanding the technologies that drive real-time interactions is crucial. Two such technologies, WebSocket and WebRTC, play pivotal roles in enabling seamless communication experiences. Whether you're a customer service expert or a developer, knowing the differences and use cases of these technologies can significantly impact your operations.
WebSocket and WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) are both designed to facilitate real-time communication, but they serve different purposes and have distinct features. This blog post delves into a comprehensive comparison of WebSocket vs WebRTC, exploring their advantages, disadvantages, and ideal use cases. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of which technology suits your needs best and how they can be integrated to enhance customer service operations.
WebSocket is a bidirectional communication protocol that allows real-time, full-duplex communication between clients and servers. Unlike traditional HTTP, which operates on a request-response model, WebSocket establishes a persistent connection, enabling efficient and continuous data exchange.
The architecture of WebSocket is based on a client-server model that aims at retaining persistent communication between a client and server. To establish a connection, the WebSocket requires the clients to initiate a handshake. During this handshake, the client (browser or device) sends a request to upgrade its protocol from HTTP to a WebSocket protocol. If the server approves the upgrade, a persistent connection that allows data to flow both ways (bidirectional) is established, enabling real-time communication and low-latency data transmission.
WebSocket provides several advantages that make it a popular choice for real-time communication:
However, WebSocket does have some limitations:
WebRTC, or Web Real-Time Communication, is a powerful technology that enables real-time communication directly within web browsers. It comprises three main components: MediaStream, RTCPeerConnection, and RTCDataChannel. These components work together to capture, transmit, and exchange audio, video, and data streams between browsers without the need for additional plugins or software installations.
WebRTC's ability to facilitate peer-to-peer communication makes it an excellent choice for applications requiring real-time audio and video streaming. However, it also comes with its own set of challenges, such as limited browser support and complexities in NAT traversal. In this section, we'll explore the core components of WebRTC, its advantages, and its limitations.
WebRTC comprises three main components that work together to enable real-time communication:
WebRTC offers several advantages that make it a compelling choice for real-time communication:
Despite its advantages, WebRTC has some limitations:
Explore what WebRTC is, how it works, and how Apizee leverages it to enhance client communication.
Learn moreWhile WebSocket and WebRTC both facilitate real-time communication, they serve different purposes and have distinct features. In this section, we'll compare WebSocket and WebRTC across various parameters to help you understand their key differences and determine which technology is best suited for your needs.
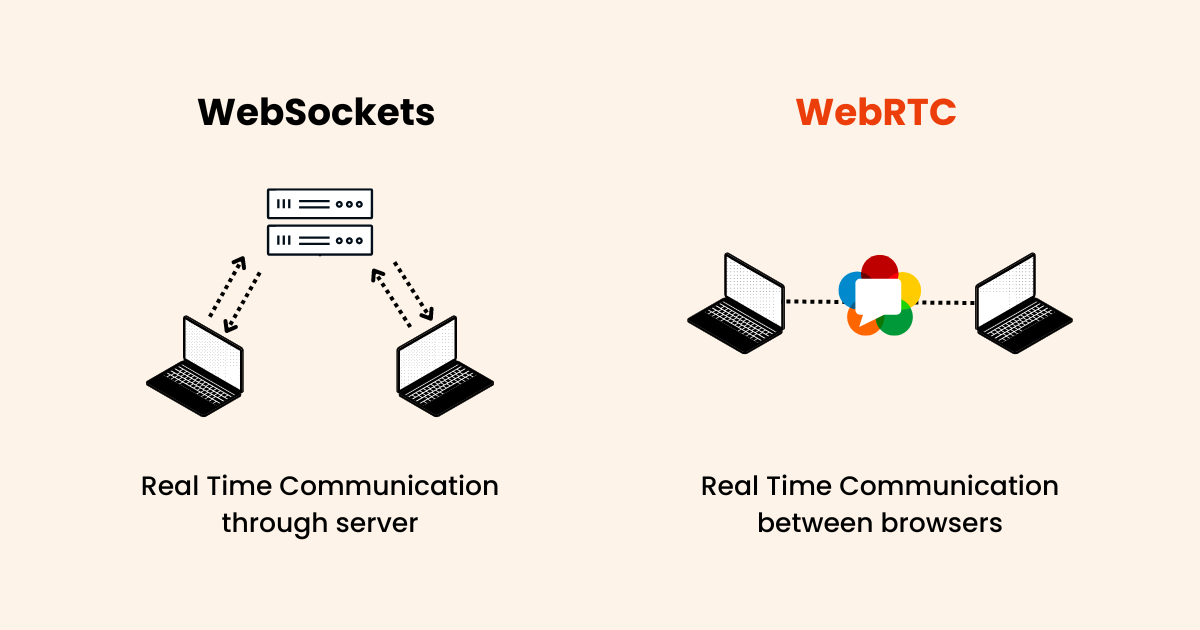
WebSocket is a bidirectional communication protocol designed for data communication, collaborative environments, and real-time chat applications. On the other hand, WebRTC is a real-time communication technology that enables peer-to-peer communication, primarily used for audio, video streaming, and video conferencing applications.
WebSocket is better suited for real-time chat applications, collaborative environments such as cobrowsing, and applications requiring continuous and simultaneous data exchange between clients and servers. WebRTC, however, is ideal for applications requiring real-time audio and video streaming, such as video conferencing, live streaming, and data transfer.
Both WebSocket and WebRTC offer low-latency communication. WebSocket provides low-latency communication for data exchange, making it suitable for real-time applications like financial trading platforms and real-time dashboards, while WebRTC is optimized for real-time audio and video streaming.
WebSocket's server-based architecture allows for higher scalability, making it ideal for large-scale real-time communication applications. In contrast, WebRTC's peer-to-peer nature can limit its scalability, making it more suitable for smaller-scale applications.
WebRTC implements encryption and authentication to protect data transmission across the internet. WebSocket also supports secure connections using SSL/TLS encryption solutions, but additional security measures, such as input validation and authentication, are necessary to prevent vulnerabilities.
WebSocket is well-suited for various implementations that need real-time, bidirectional communications. In this section, we'll explore some of the scenarios where WebSocket can be implemented, such as real-time chat applications, collaborative environments, and applications requiring continuous data exchange.
Chat applications require real-time and instant messaging where users can send or receive chats instantly. As such, WebSocket is widely used in such apps to enable instant messaging.
Collaborative applications, such as collaborative document editing and project management tools, can leverage WebSocket to enable real-time collaboration features.
Applications such as financial trading platforms and real-time dashboards that require continuous and simultaneous data exchange between clients and servers can also leverage WebSocket’s full-duplex nature.
WebRTC technology is an excellent choice for developers building applications that require real-time communication and streaming capabilities. You can group WebRTC applications into four broad categories: conversational voice and video, live streaming, data transfer, and privacy enhancement. In this section, we'll explore each of these use cases in detail.
The most popular implementation of WebRTC is for applications that need the ability to have a person communicate with others in real-time and in a conversational manner. Developers can easily implement WebRTC technology using audio and video APIs.
While WebRTC isn’t the most popular choice for streaming, it is one of the best technologies available for low-latency live streaming. If you need to stream something to one or more users and maintain really low latency to enhance the interactivity for applications such as cloud gaming, live gambling, or webinars, then WebRTC is the most efficient technology.
You can send voice and video with WebRTC, but you can also send arbitrary data. This can be used to share huge files between machines with little need for server space, for example. Or it can be used to create a BitTorrent-like experience within a video conferencing or collaborative platform.
Since WebRTC runs directly between browsers, it is sometimes used to enhance privacy. This is done by simply not sending the media or data via servers at all, ensuring a higher level of privacy for the users.
WebSocket and WebRTC work hand in hand to enhance communication features. As mentioned above, WebRTC is primarily used to enable real-time communication between devices on the internet. However, for users to experience smooth and seamless video calls, chats, and more, there has to be a server to coordinate the communication process among the devices. This coordination process is known as signaling.
Generally, signaling involves the transfer of crucial information between peers. Such information includes media metadata like codecs and various media types, network data such as IP addresses and ports, and session control messages that initiate and terminate communication. Although WebRTC facilitates real-time video conferencing and streaming features, it lacks the built-in standard signaling features. As a result, developers leverage other protocols to handle the signaling process. Here is where the WebSocket protocol comes into play.
Developers often opt for WebSocket to implement signaling in WebRTC owing to its efficient signaling mechanism to build applications such as bidirectional communication apps, collaborative environments, or real-time chat applications.
In conclusion, both WebSocket and WebRTC are powerful technologies that enable real-time communication, each with its own unique strengths and use cases. WebSocket's bidirectional communication capabilities make it perfect for real-time chat applications and collaborative environments. On the other hand, WebRTC excels in peer-to-peer audio and video streaming, making it ideal for applications like video conferencing and live streaming.
Understanding the differences between WebSocket and WebRTC, as well as their respective advantages and limitations, is crucial for making informed decisions about which technology to use for your specific needs. By leveraging the strengths of both technologies, you can create robust and efficient communication solutions that enhance customer service operations.
If you're looking to implement these technologies in your customer service operations, consider exploring the solutions offered by Apizee. With a focus on remote visual support and innovative video communication technologies, Apizee can help you transform your customer service experience and achieve higher levels of customer satisfaction.
Yes, WebSocket and WebRTC can be used together to enhance communication features. WebSocket is often used to handle the signaling process in WebRTC applications, while WebRTC is primarily used for real-time communication between devices on the internet. This combination allows for smooth and seamless video calls, chats, and more.
WebSocket is geared towards data communication, collaborative environments, and real-time chat applications, while WebRTC focuses on real-time audio, video streaming, and video conferencing applications. WebSocket establishes a persistent connection for bidirectional communication between clients and servers, whereas WebRTC enables peer-to-peer communication.
No, WebRTC is not built on WebSockets. WebRTC uses its own protocols for real-time communication, though they can work together. WebSocket is often used for signaling in WebRTC applications, but they are distinct technologies.
WebRTC is well-suited for applications requiring real-time communication and streaming capabilities. Common use cases include conversational voice and video, low-latency live streaming, data transfer, and enhancing privacy by running direct communication between browsers without involving servers.
Explore the top customer service trends for 2026—a quick look at what’s shaping customer expectations and behaviors in the year ahead.
Customer service: trends not to miss in 2026
8 Dec 2025
Here is the list of best Call Center Conferences to attend in 2026. Check out the top events, summits and meetups globally that you can plan for this year.
List of Best Call Center Conferences to Attend in 2026
1 Dec 2025
Best Customer Experience Conferences to Attend in 2026
1 Dec 2025
Interested in our solutions?